enteral vs parenteral nutrition
It is a strong and commonly held belief among nutrition clinicians that enteral nutrition is preferable to parenteral nutrition. In the low risk situations enteral feeding is more preferred than parenteral feeding.

Comparison Of Enteral And Parenteral Nutrition In Patients With Severe Download Table
The choice between enteral and parenteral nutrition In general enteral nutrition is preferred to parenteral nutrition as it is more physiological simpler cheaper and less complicated.

. Does not rely of gastricintestinal function. The enteral feeding involves the esophagus stomach and small and large intestines but the parenteral feeding involves the. Less need for interruptions.
Overcoming the Contamination Challenges Saswati Sinha1 Gunjan Lath2 Sameer Rao3 A b s t r ac t Enteral nutrition EN has host of benefits to offer to critically ill patients and is the preferred. Enteral nutrition is typically used as a short-term solution while the patient is recovering from surgery illness or an injury. With enteral nutrition1516 Finally enteral nutrition even that in volving invasive placement of gastric or jejunal tubes is approximatelly 4 to 10- fold less expensive than parenteral nutri tion.
Enteral Nutrition Monitoring XXXIV. Adjusted Body Weight XLII. Most studies reported no methods to blind personnel or outcome assessors to nutrition groups.
Calculating Nutrient Needs XLI. ENTERAL NUTRITION EN is considered to be better than total parenteral nutrition TPN for providing feeding in various clinical settings because it is less expensive safer and maintains the nutritional metabolic immunological and barrier function of the intestines. Venous Sites from which the Superior Vena Cava may be Accessed XXXVII.
The average daily cost of total parenteral nutrition TPN hereafter referred to as central parenteral nutrition. Controversy persists as to the optimal means of providing adjuvant nutritional support. Parenteral nutrition is an invasive therapy that provides nutrition support for persons who do not have adequate gastrointestinal functions.
The rationale for prescribing enteral nutrition rather than parenteral nutrition PN is based on the superior maintenance of intestinal structure and function 2 reduced infection rates 3 and reduced cost of enteral alimentation. However it does have inherent risks Enteral nutrition specifically tube feeding is the preferred method of feeding because it is cheaper has fewer complications and has better outcomes than does parenteral nutrition. The main difference between enteral and parenteral feeding is that enteral feeding is the delivery of food via the human gastrointestinal tract.
In most cases the foodstuffs are liquid and they usually come through a series of tubes and catheters. Guidelines Medicare Coverage of nutritional therapy is provided under the prosthetic device benefit provision which requires that the patient must have a permanently inoperative internal body organ or function thereof. Enteral feeding delivers liquid nutrition through a catheter inserted directly into the gastrointestinal GI tract.
To date specialized enteral nutri tional products have been developed for use in prematurity enriched with essen. Enteral nutrition EN is recommended as the preferred route for early nutrition therapy in critically ill adults over parenteral nutrition PN. Parenteral nutrition PN support is.
The aim of this study was to compare enteral nutrition EN and parenteral nutrition TPN in terms of adequacy of nutritional intake septic and nonseptic morbidity and mortality. What is the difference between enteral and parenteral routes of administration. Enteral versus parenteral nutrition.
Safe and less need for mechanical ventilation and better muscle mass if used early when relative CI to enteral nutrition Doig et al 2013 ANZICS trial Disadvantages. COMMENTARY Safety of Enteral Nutrition Practices. We provide a narrative review of more recent studies and technical reviews comparing enteral nutrition with parenteral nutrition.
Enteral nutrition EN support is the provision of nutrition using an enteral device inserted into the gastrointestinal GI tract. In contrast parenteral feeding is the delivery of food into the bloodstream bypassing the gut. A recent large randomized controlled trial RCT showed no outcome differences between the two routes.
Enteral feeding involves delivering liquid foods through a catheter inserted directly into the gastrointestinal tract whereas parenteral feeding involves providing nutrients directly into the blood stream. Can be started early. 12 Moreover it has been recently shown that patients fed via EN after abdominal surgery for.
One study used adequate methods to reduce risk of performance biasEnteral nutrition versus parenteral nutritionWe found that one feeding route rather than the other EN or PN may make little or no difference to mortality in hospital risk ratio RR 119 95 confidence interval CI. The site of entry of the tube and tube types will be discussed under enteral access Parenteral nutrition refers to the delivery of calories and nutrients into a vein. Enteral nutrition is chosen over parental for the following reasons.
Parenteral nutrition by contrast provides nutrition intravenously which means it goes directly into the bloodstream. Enteral vs Parenteral. Enteral nutrition is the process of nourishing a patient with a liquid diet of defined composition usually given through a na-sogastric nasointestinal gastrostomy or jejunostomy tube.
For patients with physical disabilities or movement disorders enteral nutrition might be used in the long. It can include a normal oral diet the use of liquid supplements or delivery by use of a tube tube feeding. Advantages of Parenteral Nutrition XXXVIII.
Parenteral nutrition is the administration of nutrients directly into the bloodstream through a central venous catheter or by peripheral infusion. No delay in caloric intake. Routes of Parenteral Nutrition XXXV.
For patients without a functional GI tract parenteral nutrition would be recommended for them as enteral nutrition would not work. However even nasogastric feeding needs care and the more complex types of enteral nutrition such as gastrostomy and jejunostomy need significant interventions. Enteral nutrition is administered through a feeding tube placed into the stomach or intestines.
Indications for Total Parenteral Nutrition XXXIX. In general enteral nutrition is preferred over parenteral nutrition when both options are on the table. Parenteral nutrition is administered through a traditional intravenous IV line or via a central IV surgically placed during an outpatient procedure.
With enteral nutrition1516 Finally enteral nutrition even that in volving invasive placement of gastric or jejunal tubes is approximatelly 4 to 10- fold less expensive than parenteral nutri tion. On either enteral or parenteral nutritional therapy depending upon the particular nature of their medical condition.

What Is The Difference Between Enteral And Parenteral Feeding Pediaa Com

Iapen Nutrition Support Therapy Enteral And Parenteral Nutrition Food Gives Energy To The Body People Need Food To Live In Some Circumstances People Cannot Eat Any Or Enough Food Due To

Enteral And Parenteral Nutrition American College Of Gastroenterology
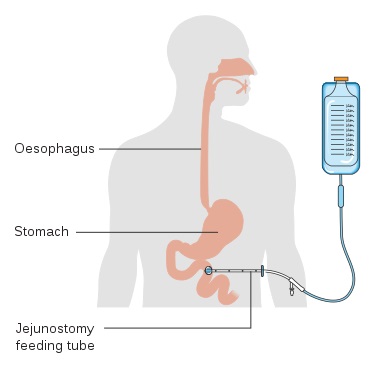
What Is The Difference Between Enteral And Parenteral Feeding Pediaa Com

Gi Enteral And Parenteral Nutrition Flashcards Quizlet
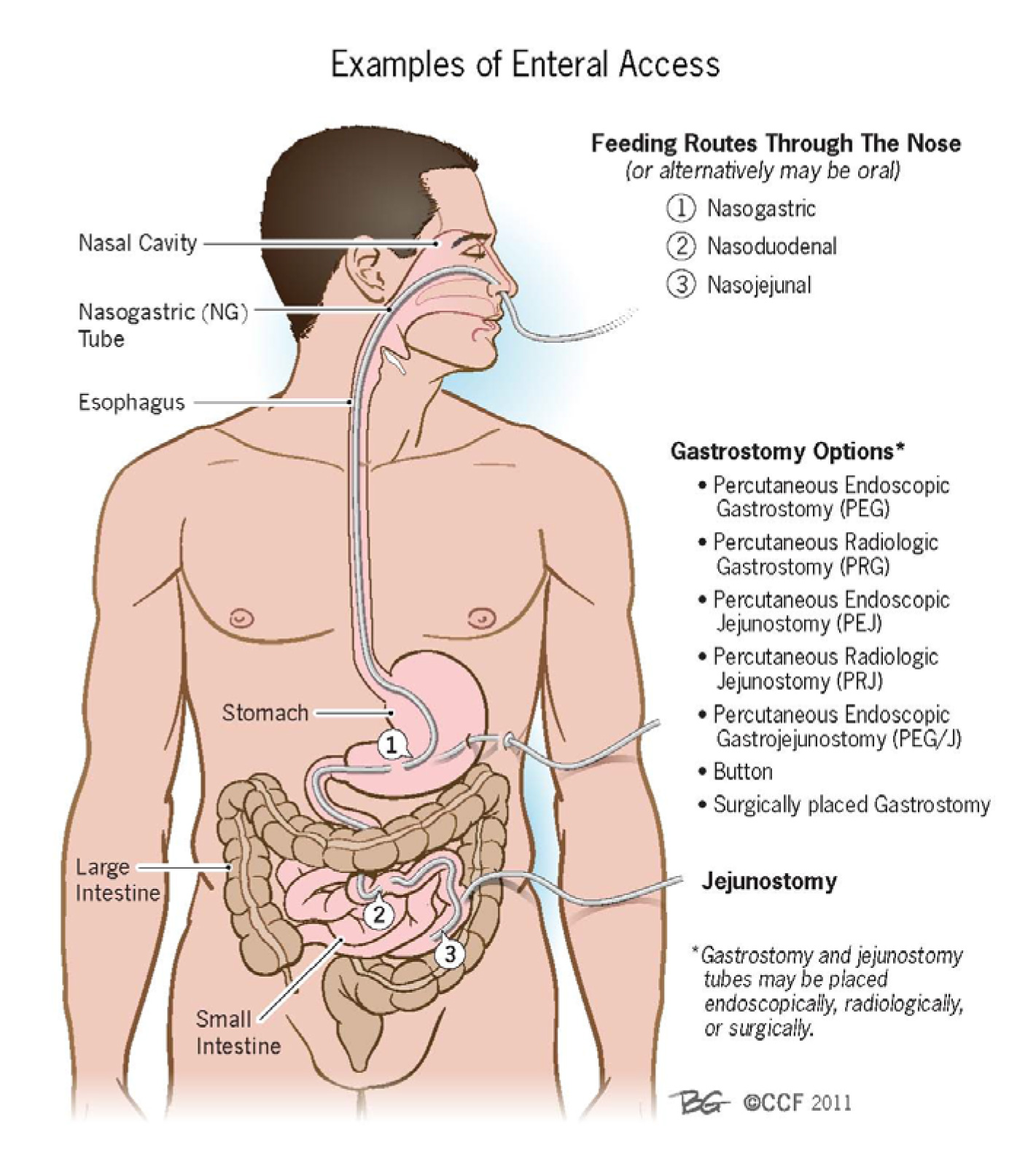
Enteral And Parenteral Nutrition American College Of Gastroenterology

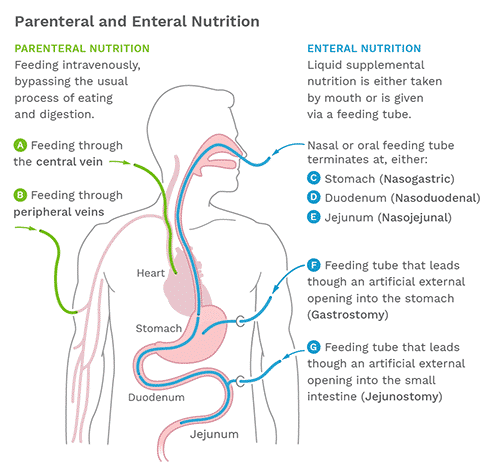
0 Response to "enteral vs parenteral nutrition"
Post a Comment